Toxic backlinks can destroy your search rankings overnight. These harmful links trigger Google penalties and damage your site’s reputation.
Every website faces toxic link threats. Competitors might attack with negative SEO. Low-quality sites might link to you without permission. Even your own past link building efforts could become toxic.
In this article, we’ll cover how to detect toxic links, get rid of them, and disavow the rest, helping you avoid penalties and recover if you’ve already been hit.
What Are Toxic & Unnatural Links?
Definition of Toxic Backlinks & Unnatural Links
Toxic backlinks are low-quality links that harm your search rankings. They violate Google’s webmaster guidelines and can trigger penalties.
Unnatural links are artificially created backlinks that don’t occur organically. These include paid links, link exchanges, and automated link building.
Google defines unnatural links as any links intended to manipulate PageRank or search rankings. This includes links from:
- Private blog networks
- Link farms
- Paid link schemes
- Low-quality directories
- Spammy comment sections
Key Characteristics of Toxic Links
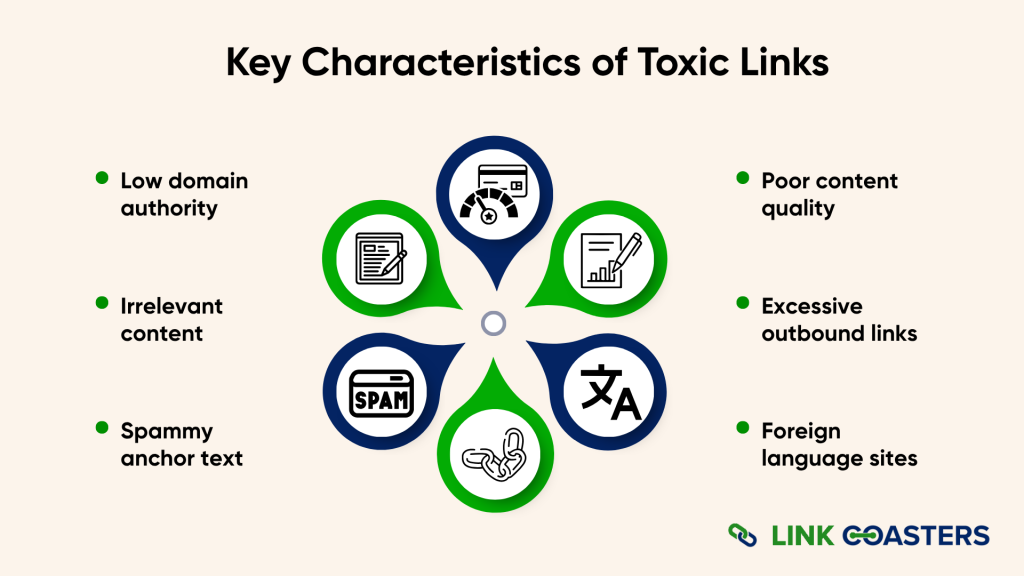
Toxic links share common warning signs that make them easy to spot:
Low domain authority: Sites with a domain authority under 20 are often low-quality sources.
Irrelevant content: Links from sites completely unrelated to your niche provide no value.
Spammy anchor text: Over-optimized or keyword-stuffed anchor text looks manipulative.
Poor content quality: Thin, duplicate, or machine-generated content indicates low-quality sites.
Excessive outbound links: Pages with hundreds of outbound links dilute link value.
Foreign language sites: Links from sites in unrelated languages often come from link farms.
Natural vs Unnatural Link Patterns
Google trusts link profiles that look organic: a variety of anchors, multiple domains, and links coming from relevant pages.
Natural link patterns include:
- Gradual link acquisition over months or years
- Varied anchor text with mostly branded terms
- Links from relevant, high-quality websites
- Editorial links within valuable content
Unnatural patterns raise red flags:
- Sudden jumps in the number of new links
- Too much exact match anchor text is showing up
- Backlinks from low-quality or unrelated websites
- Link swaps are done only for SEO purposes
- The same anchor text is repeated across multiple domains
Want to understand backlinks better? Check out our complete backlinks guide for a full overview.
How are Toxic Links Harmful for SEO?
Google Manual Action Penalties
Manual action penalties happen when Google’s human reviewers decide your site has broken the rules. Unlike algorithm updates, these can wipe out your search visibility almost overnight.
Common manual actions tied to toxic links include:
- Unnatural links to your site
- Unnatural links from your site
- Partial matches that affect only certain pages
When a manual action hits, Google will notify you in Search Console. These cases need urgent attention. The only way to recover is by cleaning up your link profile and then submitting a reconsideration request. Even if done correctly, the process can take weeks or in some cases, months before your rankings recover.
Algorithmic Ranking Downgrades
Google’s algorithms automatically detect and devalue toxic links. These algorithmic penalties happen without notification.
Penguin algorithm updates specifically target manipulative link schemes. Sites with toxic link profiles see ranking drops across multiple keywords.
Unlike manual actions, algorithmic penalties don’t show up in Search Console. You’ll only notice through ranking and traffic declines.
Loss of Organic Traffic and Visibility
Toxic links cause immediate traffic losses. Sites can lose 50-90% of organic traffic from severe penalties.
Traffic losses compound over time. Lower rankings mean fewer clicks, reduced brand visibility, and lost revenue opportunities.
Recovery takes significant time and effort. Even after cleaning toxic links, rankings may take months to recover fully.
Damaged Site Reputation & Competitive Disadvantage
Toxic links damage your site’s reputation with both users and search engines. This creates long-term competitive disadvantages.
Search engines lose trust in sites with toxic link profiles. This affects rankings for all keywords, not just targeted terms.
Competitors with clean link profiles gain advantages. They rank higher and capture more market share while you recover.
How to Identify Toxic Backlinks

Manual Toxic Link Detection
Red Flags to Look For
Start by examining your backlink profile for obvious warning signs
- Suspicious anchor text patterns: Look for over-optimized anchor text or phrases that don’t match your content.
- Low-quality source content: Check if linking pages contain thin, duplicate, or irrelevant content.
- Unrelated niches: Backlinks from websites in completely different industries can look suspicious and often point to manipulation.
- Excessive advertising: Pages overloaded with ads or affiliate links usually offer little real value to users.
- Poor site design: Outdated layouts, broken links, or neglected pages are signs of low-quality or abandoned sites.
Domain Authority Analysis
Use tools like Moz or Ahrefs to check the domain authority scores of linking sites.
Sites with DA scores under 20 require closer inspection. However, don’t automatically assume low DA means toxic.
Consider the site’s age, content quality, and relevance to your niche. New sites in your industry might have low DA but still provide value.
Content Quality Assessment
Evaluate the content that surrounds your links.
- Content depth: Strong sites publish detailed, well-researched articles that go beyond surface-level info.
- Writing quality: Look for clean writing with proper grammar, spelling, and a professional tone.
- Content freshness: Outdated articles or abandoned blogs may no longer be valuable to link from.
- Editorial standards: Reputable sites usually follow clear guidelines, fact-check their work, and maintain consistency.
Using Google Search Console & Third-Party SEO Tools
Google Search Console provides free backlink data for your website. Access the Links report to see all detected backlinks.
Export your link data and sort by linking domain. Look for patterns in low-quality sources or suspicious anchor text.
Third-party tools can give you a deeper look at link quality:
- Ahrefs: Delivers detailed link metrics and spam indicators to help spot toxic backlinks.
- SEMrush: Calculates a toxic score and automatically flags links that look suspicious.
- Moz: Provides spam scores along with domain authority to evaluate the overall strength of linking sites.
Common Sources of Toxic Links
Low-Quality Directories
Article directories and low-quality web directories often generate toxic links.
Warning signs include:
- Hundreds of unrelated categories
- Poor site organization
- Excessive advertising
- Automated submission processes
- Foreign language content
Avoid directories that accept any content without editorial review.
Spammy Blog Comments
Comment spam creates toxic links through automated posting on blogs and forums.
These links typically:
- Contain generic, irrelevant comments
- Use exact match anchor text
- Appear on unrelated blog posts
- Come from automated tools
- Include multiple outbound links
Quality blog comments require manual, thoughtful engagement with the content.
Paid Link Schemes
Buying links goes against Google’s guidelines and can quickly create a toxic backlink profile. Some common paid link schemes include:
- Guest post services that guarantee backlinks
- Private blog networks (PBNs) built just for SEO
- Link rental or “monthly link” services
- Bulk directory submissions with no real value
- Low-quality social bookmarking services
If a service promises quick and easy backlinks, those links are probably toxic and more harmful than helpful.
Link Farms
Link farms are websites built for one purpose manipulating search rankings by trading links. They don’t exist to serve real users, and Google considers them toxic.
Typical signs of a link farm include:
- Pages filled with dozens of random outbound links to unrelated sites
- Thin or no real content, often just endless link lists
- Reciprocal link swaps, where sites agree to link back to each other
- Low-quality, automated content that adds no real value
- Zero user traffic or engagement
If you come across a site that looks like this, any backlink from it is more likely to hurt than help.
Irrelevant Website Links
Links from completely unrelated websites provide no value and can appear manipulative.
Examples:
- Casino sites linking to health blogs
- Foreign e-commerce sites linking to local services
- Adult content sites linking to family businesses
- Pharmaceutical sites linking to technology companies
Toxic Link Building Practices to Avoid
Paying for Bulk Links
Bulk link purchases create obviously artificial link profiles. These services typically use:
- Private blog networks
- Low-quality guest posts
- Automated directory submissions
- Comment spam tools
Focus on earning links through quality content instead of buying them.
Low-Quality Directory Submissions
Most web directories provide little value and can create toxic links.
Avoid directories with:
- No editorial review process
- Unrelated category mixing
- Excessive advertising
- Poor site maintenance
- Automated submission acceptance
Exact Match Anchor Text Overuse
Using exact match keywords excessively creates unnatural anchor text patterns.
Natural link profiles contain mostly:
- Branded anchor text
- Generic phrases like “click here”
- Natural variations of keywords
- Page titles and descriptions
Keep exact match anchors under 5% of your total profile.
Spammy Forum & Comment Links
Automated forum and comment posting creates obvious spam signals.
Quality forum participation requires:
- Reading and understanding the discussion context
- Providing valuable, relevant contributions
- Following community guidelines
- Building genuine relationships
Hidden Link Schemes
Hidden links attempt to manipulate rankings without user awareness.
Common techniques include:
- White text on white backgrounds
- Tiny font sizes
- Links hidden behind images
- CSS positioning off-screen
These schemes violate Google’s guidelines and risk severe penalties.
Using Automated Link Building Bots
Automated tools create obviously artificial link patterns that trigger penalties.
Bots typically:
- Post identical content across multiple sites
- Use templated anchor text patterns
- Ignore site relevance and quality
- Generate volume over value
Manual, strategic link building produces better long-term results.
How to Disavow Toxic Links

Step 1: Contact Site Owners for Link Removal
Before using Google’s disavow tool, attempt manual link removal.
Create a spreadsheet documenting:
- Toxic link URLs
- Contact information for site owners
- Removal request dates
- Response status
Send polite, professional removal requests. Include specific URLs and explain why you’re requesting removal.
Allow 2-4 weeks for responses before proceeding to disavowal.
Step 2: Use Google’s Disavow Tool
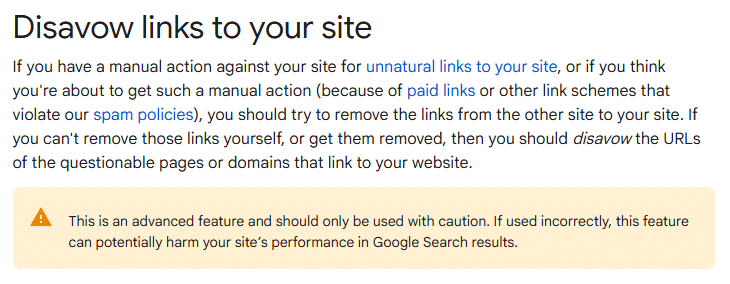
What Is the Disavow Tool?
Google’s disavow tool tells search engines to ignore specific backlinks when evaluating your site.
The tool doesn’t remove links from other websites. It simply prevents them from affecting your rankings.
Access the tool through Google Search Console under the “Disavow links” section.
When to Use the Disavow Tool
Use the disavow tool only when:
- You have a manual action penalty for unnatural links
- You’ve attempted manual removal without success
- You have clear evidence of negative SEO attacks
- You’ve identified obviously toxic links harming your profile
Don’t disavow links unless they’re clearly harmful. Over-disavowal can hurt your rankings.
Creating a Disavow File
Disavow File Format Requirements
When you create your plain text file (.txt), follow these rules:
- Put one URL or domain per line.
- Use # at the beginning of a line if you want to add a comment.
- Don’t include any extra characters, spaces, or formatting just the URLs and comments.
- Keep the file size under 2MB.
Disavowing Individual URLs
For specific page links, include the full URL:
https://example.com/bad-page.html https://spamsite.com/another-bad-page.html
Disavowing Entire Domains
For site-wide disavowal, use the domain: prefix:
domain:badsite.com domain:spamsite.net
Disavow entire domains when most or all links from a site are toxic.
Adding Comments to Disavow Files
Document your reasoning with comments:
# Contacted site owner on 2025-01-15, no response domain:badsite.com
# Low-quality directory with spam content https://directory.com/bad-page.html
Comments help track your disavowal reasoning and decisions.
Uploading to Google Search Console
Step-by-Step Upload Process
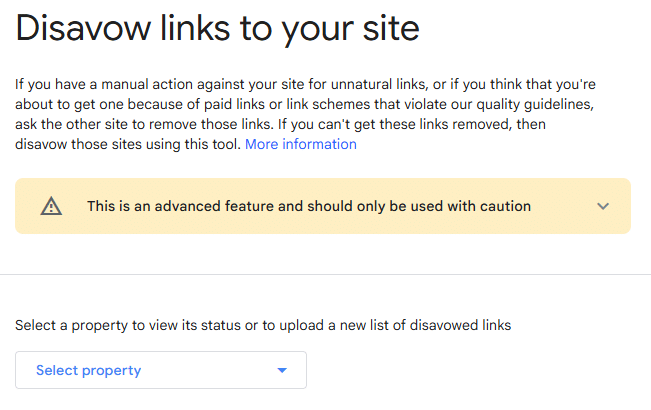
- Log in to Google Search Console.
- Choose the property (website) you want to work with.
- Go to “Disavow links” under the Legacy tools section.
- Click the “Disavow links” button.
- Upload your prepared disavow file.
- Hit “Submit” to complete the process.
Verifying File Submission
Once you’ve submitted your disavow file, double-check that everything went through correctly:
- Look for the confirmation message that appears after upload.
- Review how many URLs or domains were processed to make sure they match your file.
- Check that there were no formatting errors or rejected entries.
Processing Time Expectations
Google doesn’t process disavow files instantly; it happens as part of its normal crawling and indexing. Here’s what to expect:
- It may take a few weeks before Google recognizes the changes.
- Expect 2–3 months before you see the full impact on rankings.
- If you’re dealing with a manual action, recovery can take even longer since it requires human review.
Common Disavow Mistakes to Avoid
Overusing the Disavow Tool
Don’t disavow links that aren’t clearly toxic. Google ignores most low-quality links automatically.
Focus on obviously harmful links like:
- Paid link scheme participants
- Link farms and private blog networks
- Spam comment networks
- Completely irrelevant link sources
Disavowing Good Backlinks
Accidentally disavowing quality links can hurt your rankings.
Before disavowing, verify links are truly toxic by checking:
- Site content quality
- Relevance to your niche
- Link context and placement
- Site authority and trustworthiness
Not Attempting Link Removal First
Google recommends attempting manual removal before disavowal.
Document removal efforts in your disavow file comments. This shows a good-faith effort for reconsideration requests.
Incorrect File Formatting
Formatting mistakes stop Google from processing your disavow file. Watch for these:
- Wrong file type: Use a .txt file only.
- Extra spaces or characters: Keep lines clean and simple.
- Mixing HTTP and HTTPS: Pick one version and stay consistent.
- Missing domain: prefix: Use domain:example.com for site-wide disavowals.
Ignoring Manual Actions
Manual actions are serious and need immediate attention, no matter what Google’s algorithms are doing.
- Check Search Console regularly for manual action notifications.
- If you get flagged, start a full cleanup right away.
- Remove or disavow harmful links, then submit a reconsideration request to Google.
How to Measure Disavow Impact & Results?
Organic Rankings Monitoring
Keep track of how your keyword rankings move before and after you submit a disavow file. This helps you see whether cleaning up toxic links is actually paying off.
- Use Google Search Console to check performance data
- Set up rank tracking in Ahrefs or SEMrush
- Do quick manual checks in Google for spot testing
Stick with tracking for at least 3–6 months, since it can take that long to see the full effect.
Traffic Pattern Analysis
Check your organic traffic in Google Analytics to spot trends. Look at:
- Overall organic sessions
- How your top landing pages perform
- Conversion rates from organic traffic
- Metrics like bounce rate and time spent reading your content.
Compare traffic before and after disavowal to see improvements.
Toxicity Score Tracking
Third-party tools can help measure how “clean” your profile looks after disavowal:
- Ahrefs spam score improvements
- SEMrush toxic score reductions
- General link quality improvements
These scores aren’t perfect, but they give you a sense of progress.
Manual Action Status
If you had a manual action penalty, watch Google Search Console closely for updates:
- New or ongoing manual action notices
- Responses to your reconsideration requests
- Confirmation if a penalty gets lifted
Always keep a record of your communications with Google—it helps for future reference.
Click-Through Rate Changes
As your rankings start to bounce back, your click-through rate (CTR) should climb as well. Keep an eye on this in:
- Search Console performance reports
- Keyword-level data for your top terms
- Overall visibility in search results
When your CTR improves, it’s a good sign your cleanup is working and users are finding your pages more attractive in the results.
Conclusion
Toxic links can seriously hurt your SEO. They may trigger penalties, drag down rankings, and wipe out valuable organic traffic. That’s why regular link profile monitoring is so important, it helps you catch problems early and act before Google steps in.
Use the disavow tool carefully and only when needed. Document everything. Avoid removing quality links. Recovery takes time. Track progress and refine your strategy.
The best protection, though, is prevention. Focus on creating valuable content and earning natural, high-quality links. Ethical SEO practices will always be safer and more effective than trying to clean up after bad ones.
Key Takeaways
- Check your backlink profile often so you can catch toxic links early.
- Try removing bad links manually before turning to Google’s disavow tool.
- Format your disavow file correctly as a plain .txt file, and use comments for clarity.
- Focus only on truly harmful links—don’t waste time on marginal or harmless ones.
- Measure recovery with multiple metrics, including rankings, traffic, and CTR.
- Keep your link profile clean long term by earning natural, high-quality backlinks.
FAQs
Unnatural links are backlinks built artificially to manipulate rankings rather than earned naturally.
Toxic links are harmful backlinks from spammy, low-quality, or irrelevant sites that can hurt SEO.
Unnatural links can trigger Google penalties, reduce keyword rankings, and damage site credibility.
Use Google Search Console or SEO tools like Ahrefs to analyze backlinks, flagging low-quality or spammy sources.
Request removal from site owners or use Google’s disavow tool if removal isn’t possible.
Contact the linking sites first; if unsuccessful, disavow harmful backlinks in Google Search Console.
Create a text file listing harmful domains or URLs and upload it through Google’s disavow tool.







